HDHMR vs Plywood: Which is Better for Your Interior Design?
HDHMR vs Plywood - which is better? Compare durability, moisture resistance, price & applications. Make the right choice for your interior project.
Quick Answer
The key difference between HDHMR and plywood lies in their composition and moisture resistance. HDHMR (High-Density High Moisture Resistant) boards are engineered from compressed wood fibres with special resins, offering superior moisture resistance and uniform density. Plywood consists of cross-laminated wood veneers providing better structural flexibility and screw-holding strength. For moisture-prone areas like kitchens and bathrooms, HDHMR typically performs better, while plywood remains the preferred choice for structural applications and furniture requiring curved designs.
At a Glance: HDHMR vs Plywood Comparison
- Moisture Resistance: HDHMR significantly outperforms standard plywood in humid conditions
- Price Range: HDHMR costs approximately ₹45–75 per sq ft; BWR plywood ranges ₹55–120 per sq ft in Indian markets
- Best Application: HDHMR excels in modular kitchens; plywood suits beds, sofas, and structural work
- Workability: Plywood is lighter and easier to cut; HDHMR requires specialised tooling
- CNC Compatibility: HDHMR offers cleaner routing and edge finishing for modern furniture
- Termite Resistance: Both require chemical treatment, though HDHMR comes pre-treated more consistently
Understanding HDHMR and Plywood: Core Differences Explained
Before choosing between HDHMR and plywood for your interior project, understanding what each material fundamentally is helps make sense of their performance characteristics. Both are engineered wood products, but their manufacturing processes create distinctly different materials suited for different purposes.
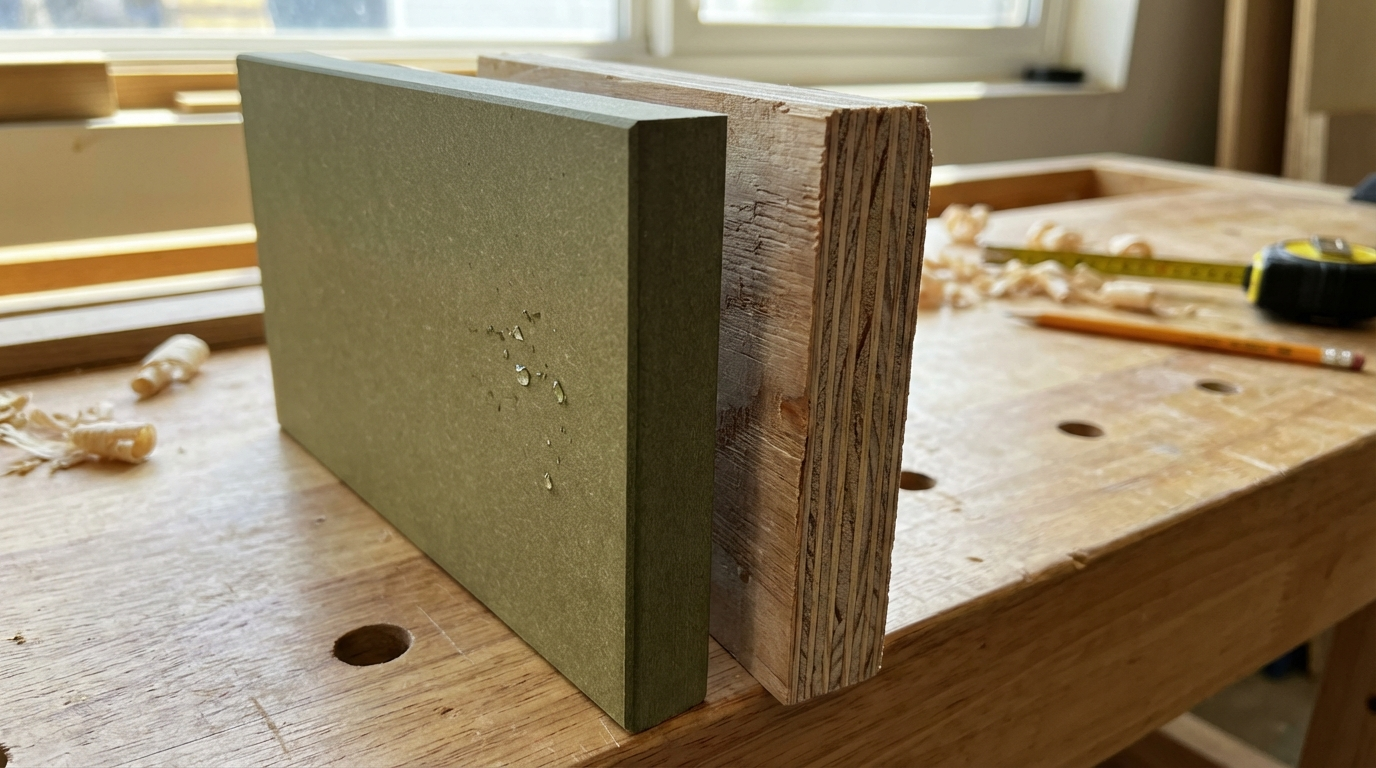
What is HDHMR Board?
HDHMR stands for High-Density High Moisture Resistant board. It is manufactured by compressing wood fibres—typically from agricultural waste, hardwood residues, and forest by-products—under extreme heat and pressure with phenolic or melamine resins. The result is a homogeneous panel with density ranging from 800 to 900 kg per cubic metre, significantly denser than most plywood variants.
The manufacturing process eliminates the natural grain structure found in solid wood, creating a uniform board that machines cleanly without splintering. This uniformity makes HDHMR particularly suitable for CNC machining and laser cutting operations common in modular furniture manufacturing. The resin infusion during production provides inherent moisture resistance, though this varies by brand and manufacturing quality.
What is Plywood?
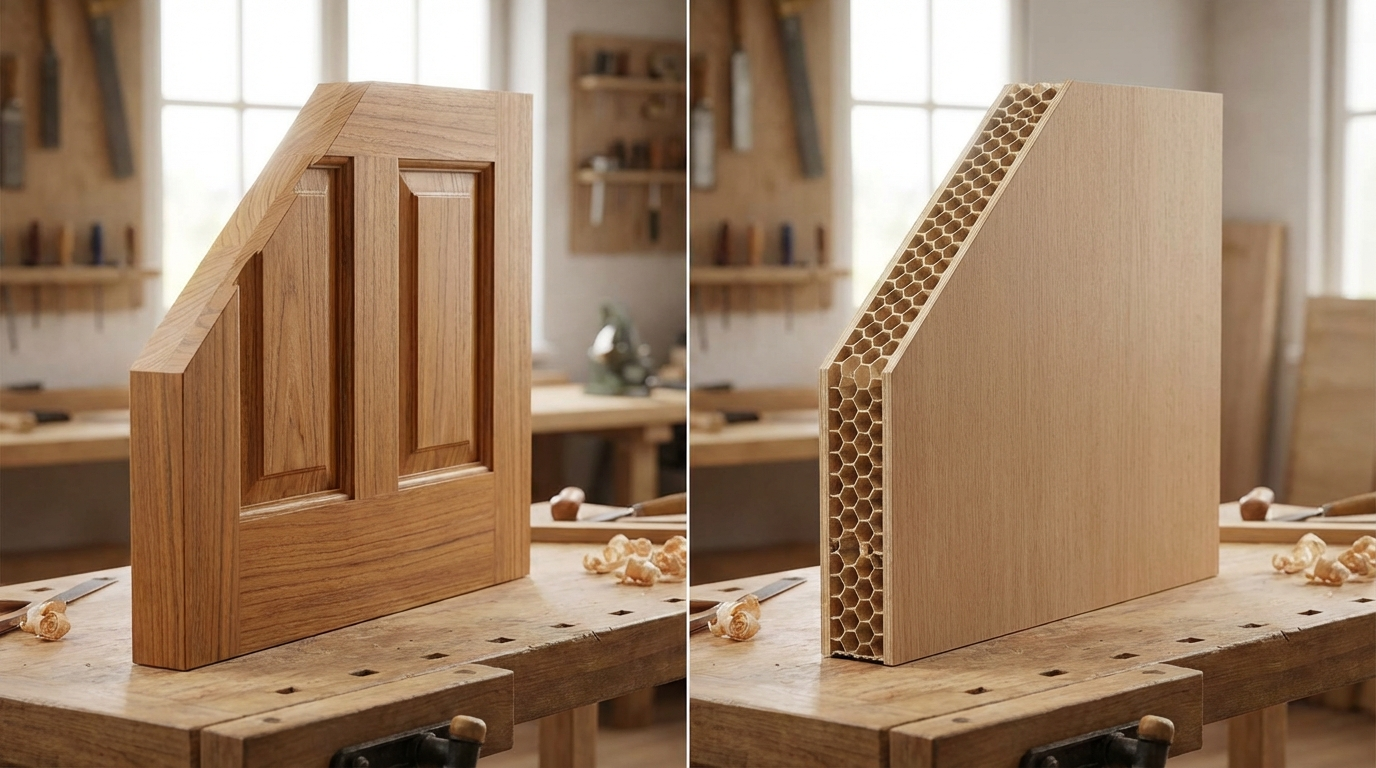
Plywood is constructed by bonding thin layers of wood veneers (called plies) with their grain directions alternating at 90 degrees. This cross-lamination technique gives plywood its characteristic strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to splitting. The core may use different wood species—commonly poplar, eucalyptus, or gurjan in India—while the face veneers determine the surface appearance and grade.
Plywood quality depends heavily on the adhesive used. In Indian terminology, MR (Moisture Resistant) grade uses urea-formaldehyde glue suitable for dry interiors, while BWR (Boiling Water Resistant) and BWP (Boiling Water Proof) grades use phenol-formaldehyde adhesives for wet areas. Marine plywood represents the highest grade, designed to withstand prolonged water exposure without delamination.
Composition and Manufacturing: How Each Material is Made
The fundamental differences between HDHMR and plywood stem from their manufacturing processes. Understanding these processes reveals why each material behaves differently in real-world applications and helps predict long-term performance.
HDHMR Manufacturing Process
HDHMR production begins with raw materials—typically wood chips, sawdust, and agricultural residues like sugarcane bagasse. These materials are broken down into fine fibres through a refining process. The fibres are then mixed with thermosetting resins and wax compounds that provide moisture resistance.
This mixture is spread onto forming lines and compressed under pressures exceeding 200 kg per square centimetre at temperatures around 180-200 degrees Celsius. The heat activates the resin, bonding the fibres into a dense, solid panel. After cooling, boards are sanded to precise thickness tolerances and cut to standard sizes. The homogeneous structure means HDHMR has consistent properties throughout its thickness—unlike plywood, which has distinct layers.
Plywood Manufacturing Process
Plywood manufacturing starts with log selection and conditioning through steam or water soaking. Logs are then peeled on rotary lathes to produce continuous sheets of veneer typically 1-3mm thick. These veneers are dried to specific moisture content before grading based on appearance and defects.
Assembly involves laying veneers with alternating grain directions and applying adhesive between each layer. The assembly is then hot-pressed at controlled temperature and pressure to cure the adhesive and bond the layers permanently. Higher-quality plywood uses more plies per thickness—an 18mm board might have 7, 9, or even 13 plies depending on quality grade. More plies generally mean better stability and strength.
HDHMR vs Plywood: Comprehensive Comparison Table
This comparison covers the primary factors Indian buyers and carpenters consider when selecting between HDHMR and plywood. Prices reflect 2024-25 market ranges across metro and Tier-2 cities, assuming standard commercial grades.
| Parameter | HDHMR Board | BWR Plywood | BWP/Marine Plywood |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 800-900 kg/m³ | 500-650 kg/m³ | 600-700 kg/m³ |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent (built-in) | Moderate | Very Good |
| Price Range (18mm) | ₹45-75 per sq ft | ₹55-90 per sq ft | ₹85-120 per sq ft |
| Screw Holding | Good on face, weak on edges | Excellent throughout | Excellent throughout |
| CNC Machining | Excellent, clean edges | Good, may chip | Good, may chip |
| Weight (18mm sheet) | Heavy (35-40 kg) | Moderate (25-30 kg) | Moderate (28-32 kg) |
| Bending Flexibility | Very limited | Good | Good |
| Termite Resistance | Usually pre-treated | Requires treatment | Usually treated |
| Standard Sizes | 8×4 ft, 7×4 ft | 8×4 ft, 7×4 ft, 6×4 ft | 8×4 ft, 7×4 ft |
| Best Application | Kitchen cabinets, bathroom vanities | Furniture, partitions | Marine applications, wet areas |
Performance Comparison: Strength, Durability and Moisture Handling
Real-world performance determines which material actually serves your project better. Laboratory specifications only tell part of the story—how materials behave over years of use in Indian climatic conditions matters far more.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
HDHMR's high density translates to impressive compressive strength and resistance to surface impacts. The board resists dents and surface damage better than most plywood grades. However, this density comes with brittleness—HDHMR can crack under sudden impact loads that plywood would absorb through its layered structure.
Plywood's cross-laminated construction provides superior tensile strength and flexibility. It handles dynamic loads better, making it preferable for shelving that will bear heavy books or kitchen drawers subject to repeated opening forces. The wood grain structure also provides better screw-holding power, particularly on edges—a critical consideration for furniture assembly.
Moisture Resistance in Indian Conditions
India's monsoon climate and coastal humidity test any wood product's moisture resistance. HDHMR generally handles consistent humidity better than standard MR-grade plywood, maintaining dimensional stability in moderately humid kitchens and bathrooms. However, it can swell irreversibly if water penetrates cut edges or screw holes that haven't been properly sealed.
BWR and BWP plywood grades handle occasional water exposure well, though prolonged submersion will eventually cause delamination. In coastal cities like Mumbai, Chennai, or Kochi, higher-grade plywood or HDHMR with proper edge-banding remains essential. Standard MR plywood should be avoided entirely in such environments.
Long-Term Durability Considerations
Over a 5-10 year period, both materials can perform excellently if specified correctly. HDHMR faces risks from edge damage—once moisture penetrates, swelling spreads from the point of entry. Plywood faces delamination risks if adhesive quality is compromised, particularly in poorly manufactured boards where glue lines weren't properly cured.
In practical terms, HDHMR cabinets in well-ventilated kitchens typically maintain appearance better than equivalent plywood installations. However, plywood furniture in living rooms and bedrooms often outlasts HDHMR equivalents because these areas experience less moisture stress.
Application Guide: Choosing the Right Material for Each Use
Material selection should always start from the application, not the material. What you're building, where it will be installed, and how it will be used determine whether HDHMR or plywood serves better.
Modular Kitchen Cabinets
HDHMR has become the preferred material for factory-manufactured modular kitchens across India. Its uniform density allows precise CNC cutting for modern handle-less designs and integrated hinges. The smooth surface accepts laminate and veneer finishes without telegraphing irregularities. Major modular kitchen brands typically use 18mm HDHMR for carcasses with appropriate edge-banding.
Plywood remains common in carpenter-made kitchens, particularly in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities where HDHMR availability is inconsistent. BWR-grade plywood with proper lamination works adequately for kitchen cabinets, though it requires more careful edge treatment and may show surface imperfections through thin laminates.
Bathroom Vanities and Wet Area Furniture
For bathroom installations, HDHMR's inherent moisture resistance provides significant advantages. Vanity units, under-sink cabinets, and storage near shower areas benefit from HDHMR's ability to handle humidity without regular swelling and warping cycles. However, direct water contact must still be prevented through proper design and sealing.
Marine-grade plywood offers a viable alternative, though at higher cost. Standard plywood grades should be completely avoided in bathroom applications regardless of waterproofing claims—the adhesive breakdown in humid conditions leads to delamination within 2-3 years typically.
Bedroom Furniture and Wardrobes
Both materials work well for bedroom furniture, making cost and carpenter familiarity the deciding factors. Plywood wardrobes have a longer track record, and most carpenters understand plywood construction techniques thoroughly. The material's lighter weight also makes handling large wardrobe panels easier during installation.
HDHMR offers advantages for wardrobe interiors where accessories like soft-close drawer systems and pull-out trays require precise mounting. The dense, uniform substrate holds hardware more predictably than plywood where screw placement might intersect with void spots or softer core materials.
Structural and Load-Bearing Applications
For any structural application—flooring underlayment, roof sheathing, wall panelling in frame construction—plywood remains the appropriate choice. Its superior flexibility, screw-holding capacity, and resistance to point loads make it suitable where HDHMR would crack or fail. This includes bed frames, sofa structures, and any application involving significant weight or dynamic loading.
Price Guide: HDHMR and Plywood Costs in India
Pricing for both materials varies significantly based on thickness, brand tier, city, and market conditions. These ranges represent typical dealer prices in 2024-25, excluding GST and transport. Actual prices in your location may vary by 15-25 percent depending on local market dynamics.
HDHMR Pricing Structure
HDHMR prices in India typically range from ₹40 to ₹80 per square foot for standard 18mm commercial grade sheets. Premium branded HDHMR from established manufacturers commands ₹65-80 per square foot, while budget options from smaller manufacturers may sell for ₹40-55 per square foot. The price difference reflects density consistency, moisture resistance quality, and surface finish.
Standard sheet sizes of 8×4 feet (32 square feet) mean a single HDHMR sheet costs approximately ₹1,400-2,500 depending on grade. Metro cities generally have better availability but not necessarily lower prices—transport costs from manufacturing hubs even out regional differences to some extent.
Plywood Pricing Structure
Plywood pricing shows greater variation due to the multiple grades available. MR-grade commercial plywood starts around ₹35-50 per square foot for 18mm thickness. BWR-grade plywood suitable for moderate moisture exposure ranges from ₹55-90 per square foot. BWP and marine-grade plywood commands ₹85-130 per square foot depending on brand and core wood quality.
An important consideration: plywood pricing often involves "trade sizes" where nominal 18mm boards may measure 17mm or 19mm depending on manufacturer practices. Always verify actual thickness before comparing prices across brands.
Total Project Cost Considerations
Material cost represents only part of total project expense. HDHMR's heavier weight increases transport costs and handling labour. Its density requires carbide-tipped blades and slower cutting speeds, potentially increasing fabrication costs. Edge-banding becomes essential rather than optional, adding ₹15-30 per running metre to finishing costs.
Plywood's familiarity to carpenters often results in lower labour costs, particularly outside metro areas. Standard woodworking tools suffice for cutting and shaping. However, plywood's surface preparation requirements for laminate application may partially offset these savings in high-quality furniture work.
How to Choose Between HDHMR and Plywood
Making the right choice requires evaluating your specific project requirements against each material's strengths. This decision framework helps navigate the selection process systematically.
Decision Criteria Checklist
- Moisture Exposure Level: High moisture environments favour HDHMR; dry areas can use either material
- Manufacturing Method: Factory CNC production suits HDHMR; site carpentry typically favours plywood
- Budget Constraints: Standard plywood offers lower entry cost; total cost differences narrow with higher-grade materials
- Local Availability: Confirm material availability with local dealers before specifying
- Carpenter Familiarity: Assess whether your fabricator has experience with HDHMR
- Design Requirements: Curved or bent components require plywood; flat-panel modern designs suit HDHMR
- Hardware Mounting: Heavy hardware loads favour plywood's screw-holding capacity
When HDHMR is the Better Choice
Choose HDHMR for modular kitchen installations, bathroom vanities, utility room cabinets, and any furniture destined for consistently humid environments. It excels in modern designs featuring flat panels, clean edges, and factory-applied finishes. If your project involves CNC fabrication and professional edge-banding, HDHMR delivers superior results.
When Plywood is the Better Choice
Choose plywood for bedroom furniture, living room units, structural applications, and any design requiring curved or bent components. It suits carpenter-made furniture where site fabrication occurs with standard tools. For projects in Tier-2 or Tier-3 cities where HDHMR availability is limited, quality BWR plywood remains the reliable option.
When NOT to Choose Each Material
Avoid HDHMR for structural applications, furniture requiring screw fixings into edges, outdoor or semi-outdoor use, and applications where the budget cannot accommodate proper edge-banding. Never use HDHMR where direct water contact is possible—even moisture-resistant grades fail under submersion.
Avoid standard plywood for wet-area installations, applications demanding perfectly smooth surfaces for thin laminates, or environments with sustained high humidity. Never use MR-grade plywood in kitchens, bathrooms, or coastal locations regardless of cost savings promised.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Materials
Experience reveals recurring errors that compromise furniture quality and longevity. Recognising these mistakes helps prevent costly failures in your projects.
Mistake 1: Ignoring Edge Treatment for HDHMR
HDHMR's moisture resistance applies to its surfaces but not cut edges. Exposed edges absorb water rapidly, causing swelling that spreads through the board. Every HDHMR edge must receive proper treatment—PVC edge-banding being the most common solution. Skipping this step to save costs inevitably leads to premature failure in kitchen and bathroom installations.
Mistake 2: Assuming All Plywood Grades are Interchangeable
Specifying "plywood" without grade designation invites substitution with cheaper materials. MR-grade plywood installed in kitchens will fail. Always specify BWR or BWP grade in writing and verify material on delivery. Check for ISI marking and manufacturer stamps on board edges as basic verification.
Mistake 3: Overestimating HDHMR's Edge Screw-Holding
HDHMR holds screws excellently on flat faces but poorly on edges. Cabinet designs requiring edge-fixed hinges or side-mounted hardware often fail when HDHMR is used without proper reinforcement. Either redesign for face-mounting or use plywood reinforcement blocks at hardware locations.
Mistake 4: Neglecting Thickness Verification
Both materials commonly show variation between stated and actual thickness. An 18mm board might measure 16.5mm or 19mm depending on manufacturer. This variation affects hardware fitting, shelf spacing calculations, and overall assembly precision. Always verify actual thickness before final design confirmation.
Mistake 5: Choosing Based on Price Alone
The cheapest option rarely provides best value. Budget HDHMR with inconsistent density fails earlier than quality plywood at similar price points. Similarly, premium prices don't guarantee quality—brand reputation and local dealer reliability matter more than price positioning.
Quick Inspection Checks
- HDHMR: Check for uniform density by knocking on the board—hollow sounds indicate voids; verify edge colour consistency indicating proper resin distribution
- Plywood: Examine core layers for gaps or overlaps; check edge cross-section for void-free glue lines; verify face veneer thickness and quality
- Both Materials: Measure actual thickness at multiple points; check for warping by placing on flat surface; verify sheet size matches specifications
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the full form of HDHMR?
HDHMR stands for High-Density High Moisture Resistant. The name describes two key properties of this engineered wood product—its high density achieved through compressed wood fibres, and its enhanced resistance to moisture compared to standard MDF or particleboard. Some manufacturers also use terms like HDHMR board or HDHMR sheet interchangeably. The material falls between MDF and plywood in the engineered wood spectrum, offering specific advantages for interior applications in humid environments.
Which is better for kitchen cabinets: HDHMR or plywood?
For modular kitchen cabinets manufactured with CNC machinery, HDHMR generally performs better due to its superior moisture resistance and uniform density that machines cleanly. For carpenter-made kitchens, BWR or BWP grade plywood remains a reliable choice, particularly in areas where HDHMR availability is limited. The critical factor is proper edge-banding for HDHMR and appropriate grade selection for plywood—either material can last 10-15 years when correctly specified and installed.
What is the price of HDHMR board per square foot in India?
HDHMR board prices in India typically range from ₹45 to ₹80 per square foot for 18mm thickness, depending on brand, quality grade, and location. Premium brands from established manufacturers command prices at the higher end, while budget options from smaller manufacturers may sell for ₹40-55 per square foot. Metro cities often have better availability but not necessarily lower prices. Always factor in edge-banding costs (₹15-30 per running metre) when calculating total project costs.
Can HDHMR be used in bathrooms?
Yes, HDHMR is suitable for bathroom vanities, cabinets, and storage units due to its inherent moisture resistance. However, it should not be exposed to direct water contact or prolonged submersion. Proper installation requires complete edge-banding of all cut edges, adequate ventilation in cabinet interiors, and avoiding designs where water can pool. For areas with direct water exposure like shower enclosures, alternatives like marine plywood or water-resistant MDF with waterproof coatings are more appropriate.
Is HDHMR stronger than plywood?
HDHMR has higher density and compressive strength, making it more resistant to surface dents and impacts. However, plywood offers superior tensile strength, flexibility, and screw-holding capacity due to its cross-laminated wood veneer construction. For structural applications requiring load-bearing capacity or designs with curved components, plywood is stronger. For flat-panel furniture requiring dimensional stability in humid conditions, HDHMR performs better. Neither material is universally "stronger"—the appropriate choice depends on the specific application requirements.
How can I check HDHMR quality before buying?
Quality HDHMR should have uniform density throughout—knock on the board surface and listen for consistent, solid sounds rather than hollow spots indicating voids. Examine the cut edge for even colour distribution showing proper resin penetration. The surface should be smooth without undulations or rough patches. Check actual thickness with a calliper, as variations from stated thickness indicate manufacturing inconsistency. Reputable brands typically display density specifications and moisture resistance ratings—look for density above 850 kg per cubic metre for quality boards.
Does HDHMR need termite treatment?
Most commercial HDHMR boards come pre-treated with termite-resistant chemicals during manufacturing. However, treatment quality varies by manufacturer, and the presence of treatment isn't always clearly stated. For installations in termite-prone areas—common across much of India—additional treatment provides insurance against infestation. Pre-treatment involves applying borate solutions to cut edges and drill holes before assembly. Unlike solid wood, HDHMR's dense composition offers some natural resistance, but treatment remains advisable for long-term protection.
Which plywood grade is equivalent to HDHMR for moisture resistance?
BWP (Boiling Water Proof) and Marine grade plywood offer moisture resistance comparable to or exceeding HDHMR. These grades use phenol-formaldehyde adhesives that maintain bond strength even under prolonged moisture exposure. However, they cost significantly more than HDHMR—typically ₹85-130 per square foot compared to HDHMR's ₹45-80 range. Standard BWR (Boiling Water Resistant) grade provides moderate moisture resistance adequate for many kitchen applications but falls short of HDHMR's performance in consistently humid environments.
Disclaimer: This content is provided for general informational purposes based on industry practices and publicly available information. Product specifications, standards, prices, and availability may vary by manufacturer, region, and time. Readers should independently verify details with manufacturers, dealers, or qualified professionals before making purchase or construction decisions.Want Plywood Suggestions?
Share a few details and a Apple Ply specialist will suggest suitable brands and connect you to responsive dealers.


